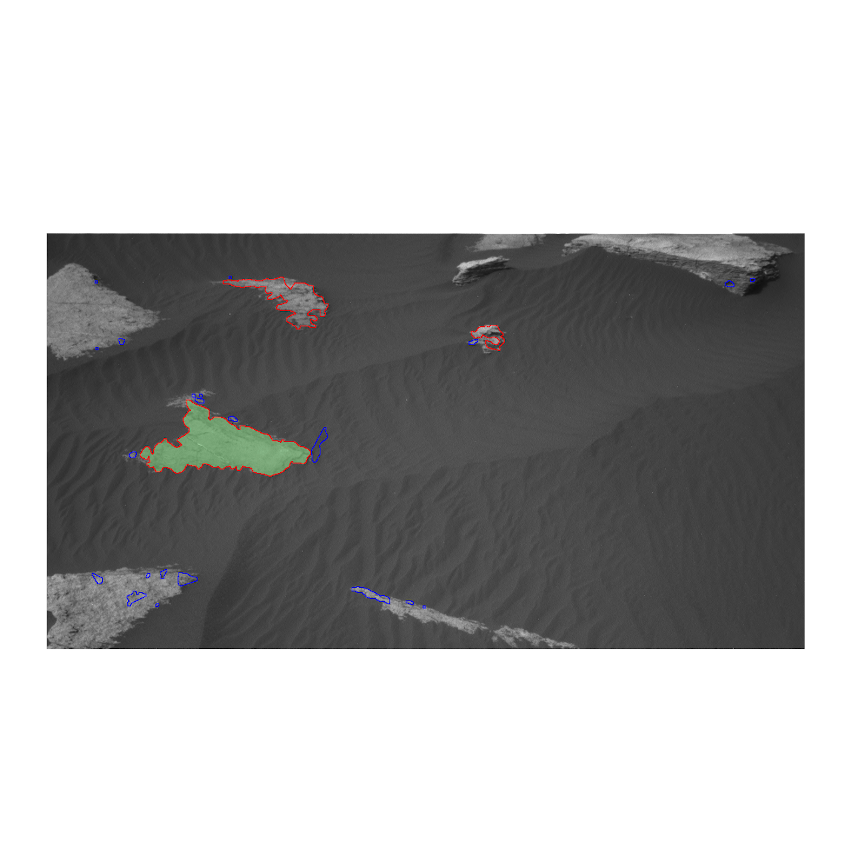
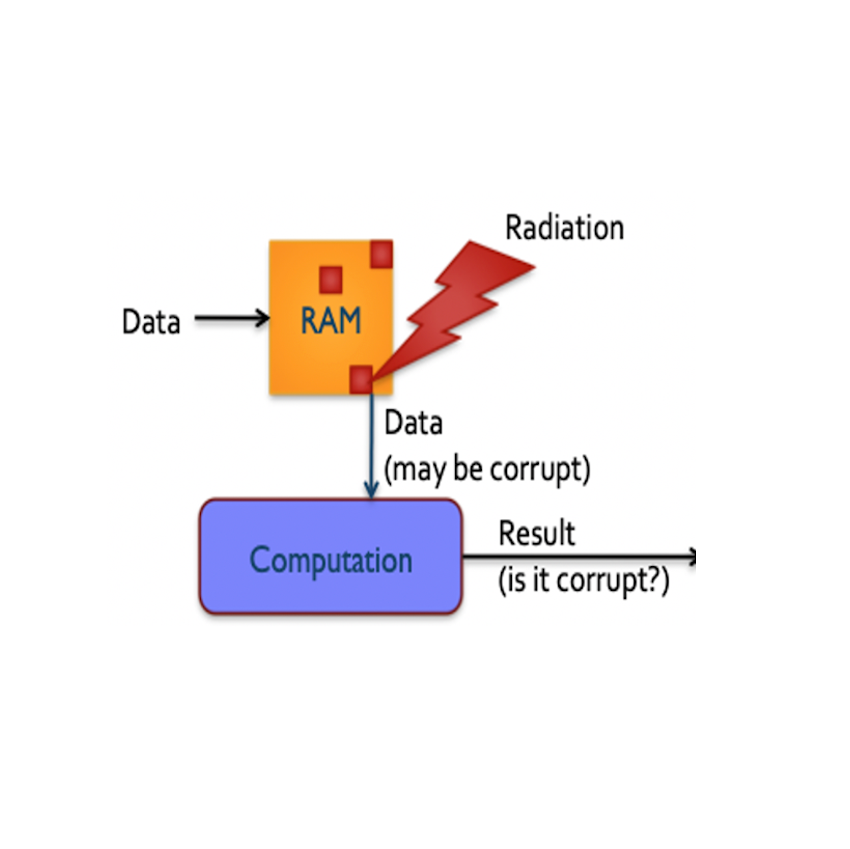
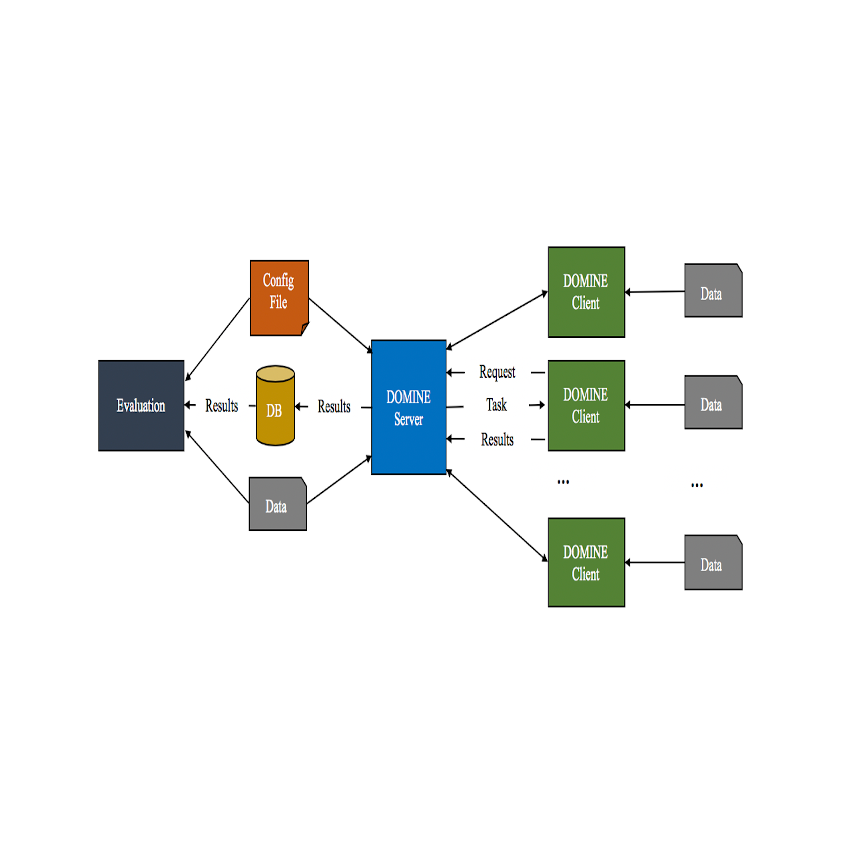
Products
As MLIA addresses our many investigations and provided solutions, we endeavor to create reusable, generalizable technology that may be applied to follow-on maturation or transferred to other projects. MLIA also invests in internal technology that speeds and makes robust our development and analysis process. These are MLIA’s Products that we maintain, mature, leverage on new tasks, and share with other research groups to enrich the development of JPL’s data-driven analysis capabilities.
Please visit our public GitHub to see a full collection of our open sourced software packages.